In the domain of dynamic Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) for novel view synthesis, current state-of-the-art (SOTA) techniques struggle when the camera's pose deviates significantly from the primary viewpoint, resulting in unstable and unrealistic outcomes. This paper introduces Expanded Dynamic NeRF (ExpanDyNeRF), a monocular NeRF method that integrates a Gaussian splatting prior to tackle novel view synthesis with large-angle rotations. ExpanDyNeRF employs a pseudo ground truth technique to optimize density and color features, which enables the generation of realistic scene reconstructions from challenging viewpoints. Additionally, we present the Synthetic Dynamic Multiview (SynDM) dataset, the first GTA V-based dynamic multiview dataset designed specifically for evaluating robust dynamic reconstruction from significantly shifted views. We evaluate our method quantitatively and qualitatively on both the SynDM dataset and the widely recognized NVIDIA dataset, comparing it against other SOTA methods for dynamic scene reconstruction. Our evaluation results demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance.
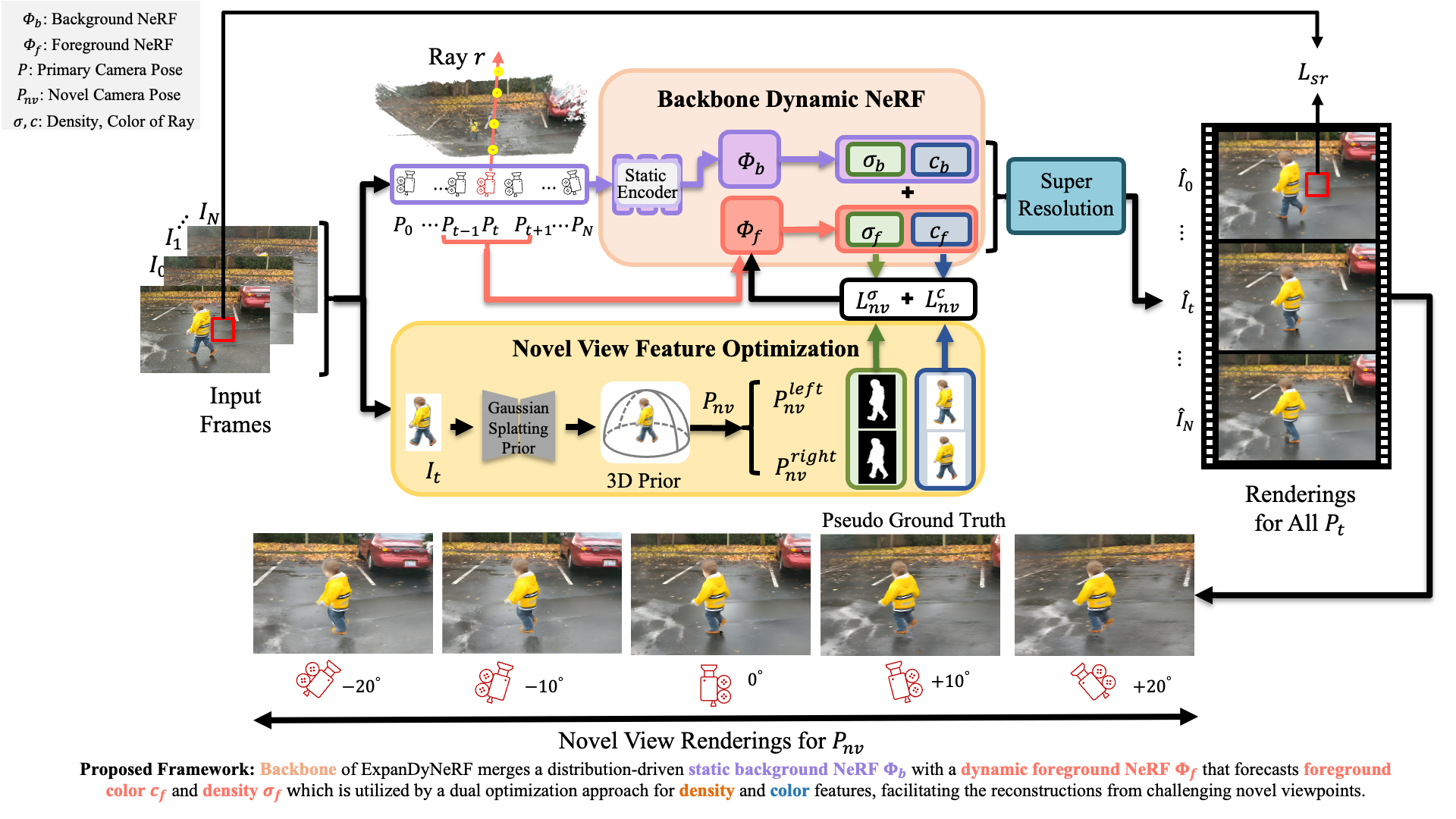
Foreground-Background Decomposition
In video sequences, backgrounds are largely static while foregrounds
are dynamic. Thus, the model decomposes the scene into two parts:
Rendered outputs from both branches are blended to reconstruct the dynamic scene, supervised by the super-resolution loss ( Lsr ).
Novel View Feature Optimization
Motivation
Existing dynamic video datasets lack ground-truth for side views,
making it impossible to quantitatively evaluate novel view synthesis
results at deviated angles. This limitation arises because recording
dynamic multi-view videos in real-world settings is extremely
difficult or nearly infeasible.
SynDM fills this gap by providing dynamic multi-view videos with side-view ground-truth, enabling systematic evaluation of novel view rendering performance.
Dataset Overview
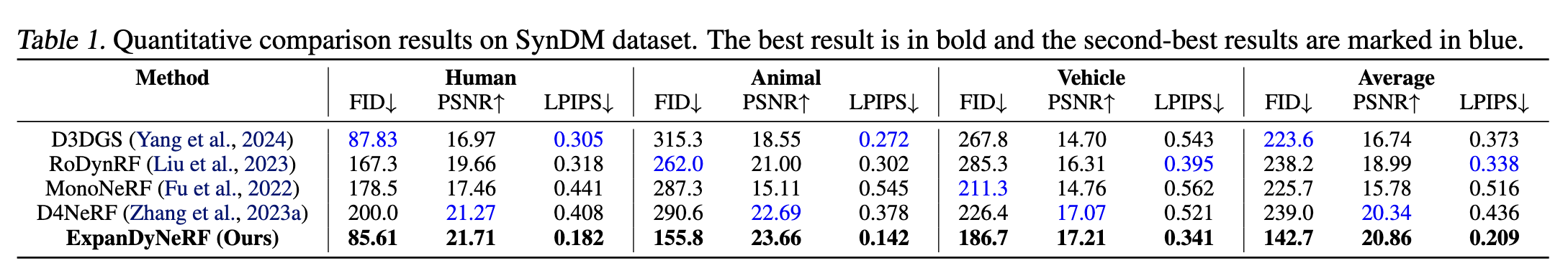
We conduct a comprehensive comparison between our ExpanDyNeRF and four SOTA novel view synthesis methods: RoDynRF (Liu et al., 2023), MonoNeRF (Fu et al., 2022), D3DGS (Yang et al., 2024), and D4NeRF (Zhang et al., 2023a), on SynDM and NVIDIA datasets. Qualitative results are shown in the video below with novel view deviated from -30 degree to 30 degree, and Quantitative results are shown in Table 1 via FID score, PSNR, and LPIPS. Our method achieves the best performance on both datasets.
Limitations of NeRF-based Methods
Advantages of Gaussian Splatting
Expanded Dynamic Gaussian Splatting (ExpanDyGauss)
To address these issues, we propose ExpanDyGauss, a monocular Gaussian splatting framework for large-angle novel view synthesis. ExpanDyGauss leverages a video-to-video diffusion model to perform spatial-temporal inpainting, generating consistent pseudo ground truth across 360°, providing effective supervision for both static and dynamic components without significant overhead.
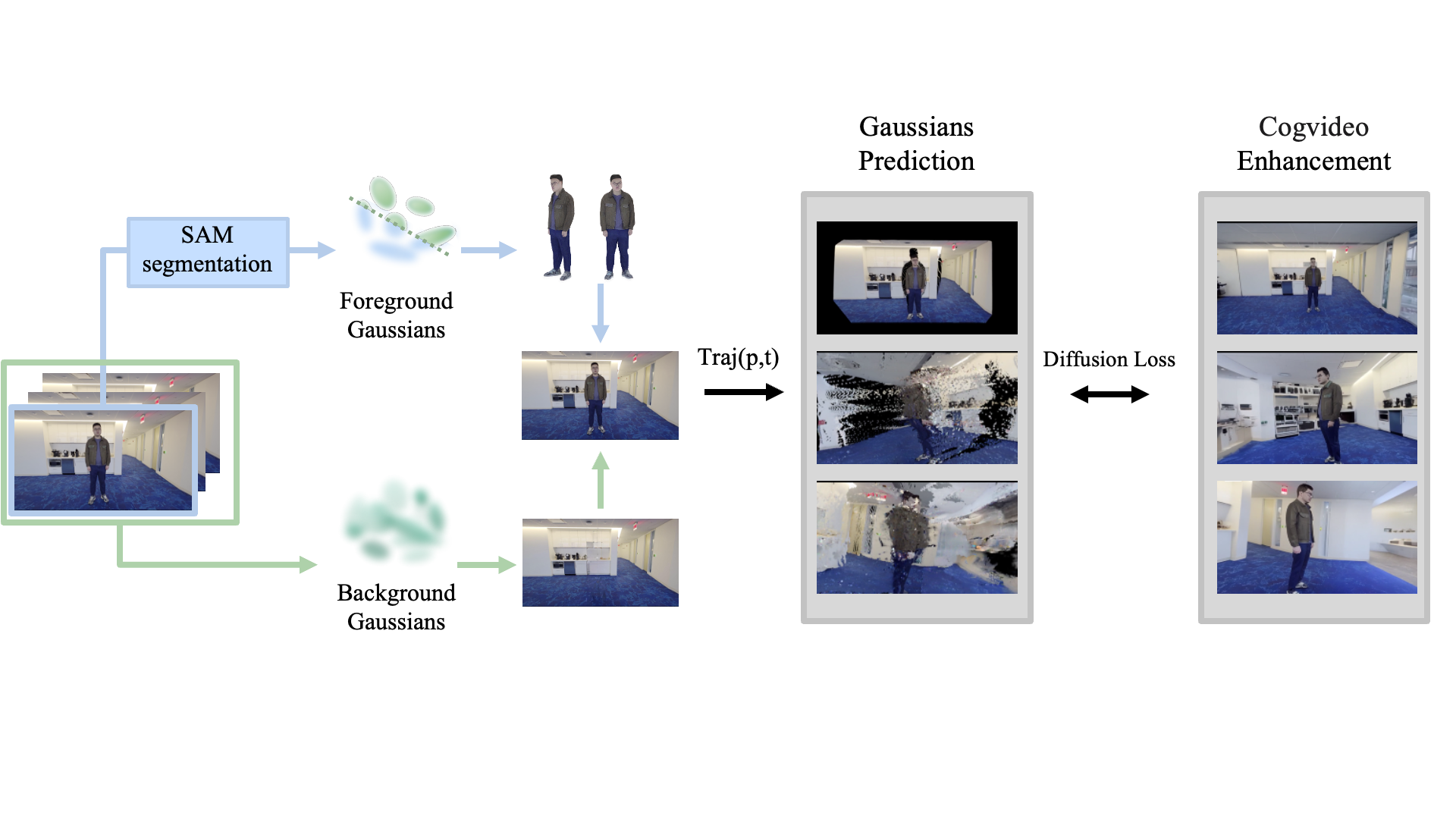
Dense Initialization and Segmentation
easi3r predicts dense 3D point clouds and camera poses from monocular videos without large camera motion.
SAM segmentation separates frames into foreground and background, forming foreground Gaussians and background Gaussians.
Gaussian Reconstruction and Enhancement
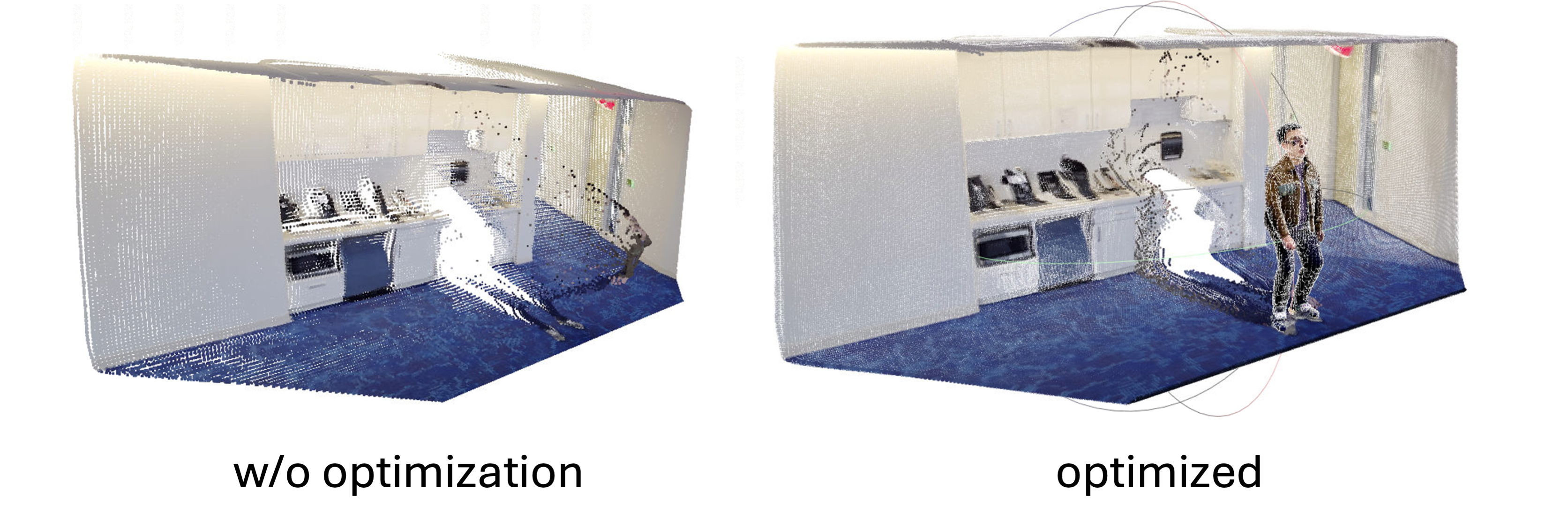
Our method generates dynamic Gaussian Splatting models for novel view synthesis on both synthetic datasets and real-world captured videos. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in handling different scenarios.
Real-world Data
To demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in the real world
application, we applied our method on a casually captured monocular
video. Our approach can generate a dynamic Gaussian Splatting model for
reasonable novel view synthesis in real-world scenarios.
Synthesis Data
A demo of the results on SynDM dataset. For a monocular input video
with dynamic scene, our method can generate a dynamic Gaussian
Splatting model and synthesize novel views.
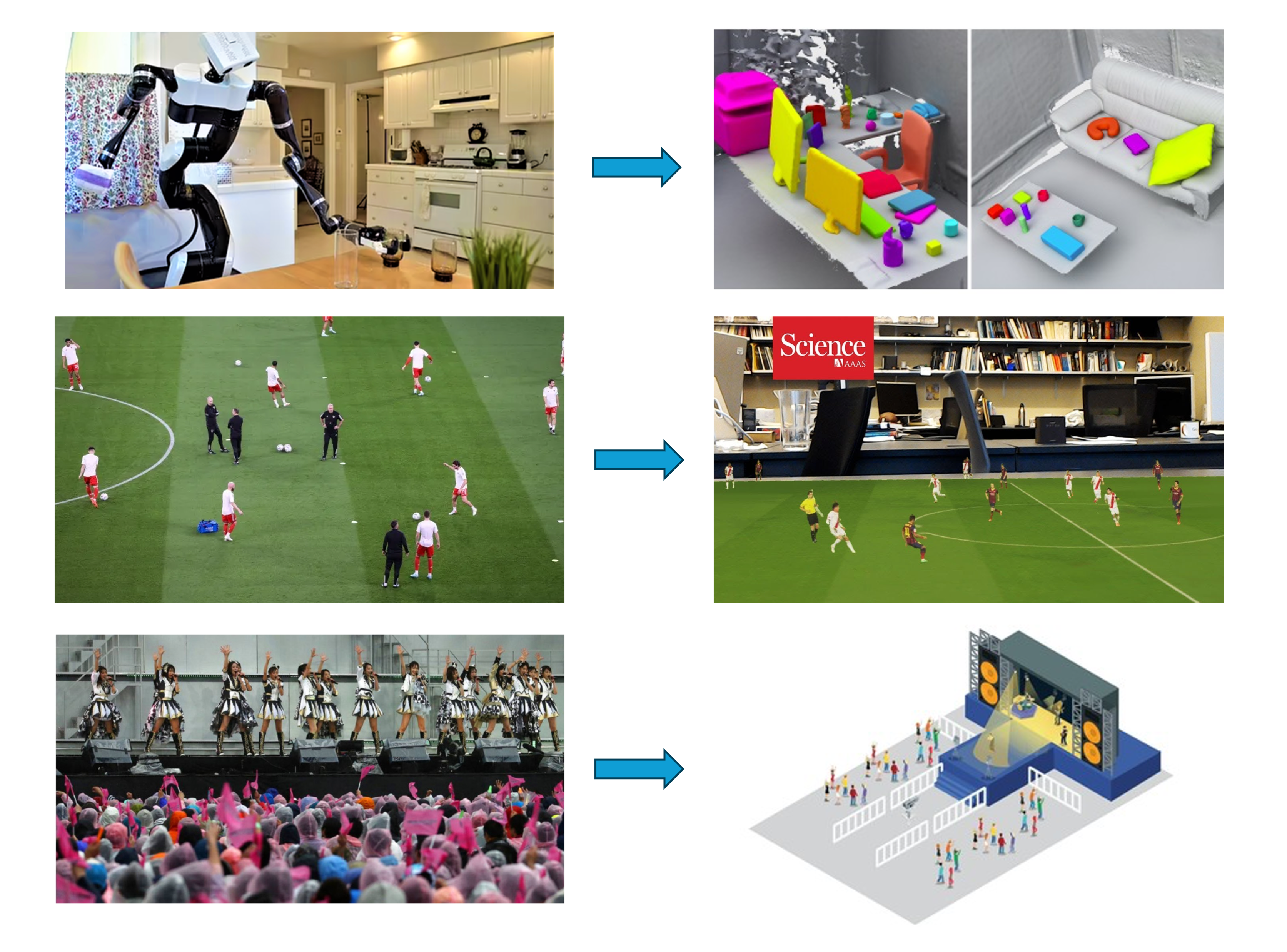
Robotic Perception and Navigation
Human Motion Capture and Sports Analysis